Exploring reference data through existing computing services for the bioinformatics community
Introduction
Galaxy is a widely adopted workflow management system for bioinformatics, aiming to make computational biology accessible to research scientists that do not have computer programming or systems administration experience.
How can scientists connect this useful, reproducibility-oriented tool seamlessly with many data sources? How can they do so in a coherent way using different instances of Galaxy? Can they run it locally or on a secured infrastructure that handles patient data? Can they compare the results of those different scenarios? Those are the main questions this use-case wants to address.
Building on top of existing French and Italian national services, the use-case will produce guidelines and best practices, and implement a service prototype based on different scientific scenarios in order to:
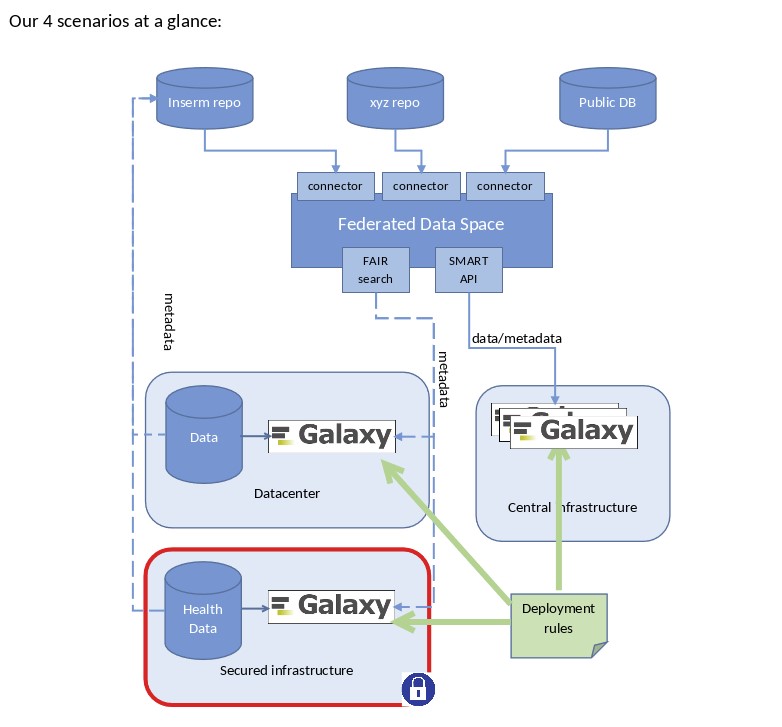
- Allow access to reference data from different Galaxy deployments within the EOSC
- Facilitate the deployment of Galaxy instances close to the data
- Provide coherency between different existing Galaxy deployments
- Ensure health data security requirements are met throughout the process

Challenges addressed
Galaxy is a widely used tool and comes in many flavours. One of the first challenges to address is the reproducibility and coherency of the different deployments to ensure that data analysis workflows produce the same results whatever the instance used. This means technical work within Galaxy itself, but also a global reflection on how to connect different data sources to Galaxy in a simple and coherent way.
Another challenge is the need to conform to data protection regulations concerning health personal data, by deploying Galaxy in a private, secured environment while still ensuring the data analysis workflow remains similar to its public counterpart.
Finally, we must find a way of providing access to the service to all users within the EOSC community through roles management and by integrating it into a global authentication framework.
Benefits through EOSC-Pillar
This use-case relies on – and demonstrates the benefits of – EOSC-Pillar services at two levels:
- Discover and get data from an EOSC-wide federated dataspace. Through 4 different usage scenarios, the use-case will build on top of the Federated FAIR Data Space (F2DS) to either collect metadata and information about datasets localisation or connect transparently to the source repositories through APIs.
- Build on top of first-class services and resources provided through the project. These are mainly:
- Laniakea – Galaxy as a service provided by INFN and CNR-IBIOM. Laniakea is a software framework that facilitates the provisioning of on-demand Galaxy instances as a cloud service over e-infrastructures.
- Data repository built by Inserm with the help and support of INRAE and CINES, around the Dataverse solution.
- Cloud Galaxy instances provided by CNRS-IFB.
- Cloud computing resources provided by different partners
- The INDIGO-IAM authentication service provided by INFN
Highlights
Results as of June 2022
- Clarification of requirements for the construction of the Federated FAIR Data Space
- Gap analysis regarding “ready-to-use” services
- Global search on the type of targeted data
- Work started on analysing legal requirements
- Definition of 4 scientific scenarios
- Public Galaxy Instance(s)
- Close-to-the-data deployment
- Health Data with restricted access
- Reproducibility and verification
- Matching of the 4 scenarios with real-life examples, taken from the hCNV community
- 2 scenarios fully implemented (close-to-the data deployment and Health Data with restricted access), 1 scenario almost complete (public galaxy instance)
- Connect source repositories and identified public databases to the Federated FAIR Data Space (F2DS)
- Set of documents produced (Galaxy deployment state of the art, common best practices, implementation report)
Next steps
- Finalise scenario 1 and scenario 4 implementation
- Finalise reporting and documentation
- Test and validate provided services and solutions